Partitioning and Mixed Models for Biodiversity Analysis in R
This catalogue respects all FAIR guidelines and best practices and uses the IEEE Standard for Learning Object Metadata (IEEE 2002) that has been customised in order to be compliant with the EOSC Training Resource Profile - Data Model.
Description
The LifeWatch eCampus offers courses, short schools and lifelong learning products dedicated to universities, post-doc and early-career researchers.
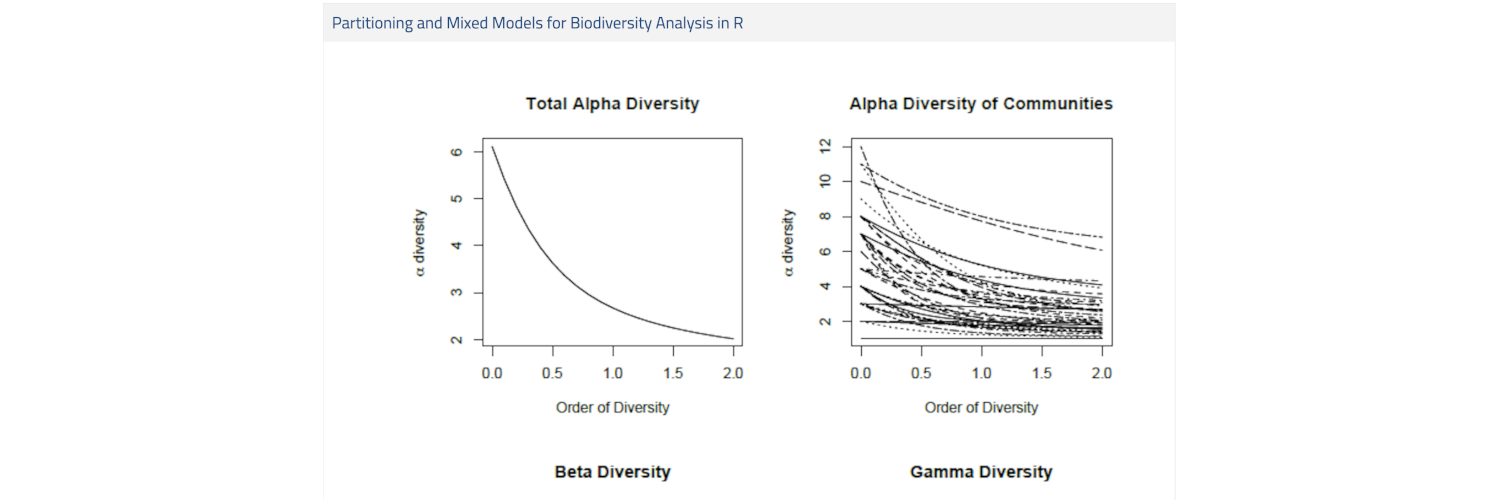
The biodiversity of all individuals in a given meta-community may be split into the diversity within and between local communities. From a conservational point of view several questions arise. What is the importance of the biodiversity of a single local community with respect to the entire metacommunity? Which local communities contribute more to the biodiversity of the meta-community? Is it possible to maintain the biodiversity of the meta-community preserving only the most diverse local communities or should we care more about the conservation of ecosystem peculiarities?
This study-lab training briefly introduces the R software and then focuses on biodiversity partitioning, describing methodology and software for γ, α and β diversity profiling. It then discusses the theory behind mixed effects modeling and how this can be applied to investigate the variation of biodiversity measures. The training concludes with a practical unit that examines the use of the R implementation of mixed effects modeling routines with data from ecological surveys.
Knowledge of α-, β- and γ-biodiversity; biodiversity and entropy; linear models; mixed effects models; basics of the R software is preferable, but not mandatory.
1 - General
2 - Life Cycle
2.3 - Contribute
3 - Educational
Students
4 - Technical
Details
| Code | 41 |
|---|---|
| Uploaded by | Maria Teresa Manca |
| Available since | 13/12/21 11:01 |
